Multispectral camera
- Post By: admin
- Date:
- Category: Instruments
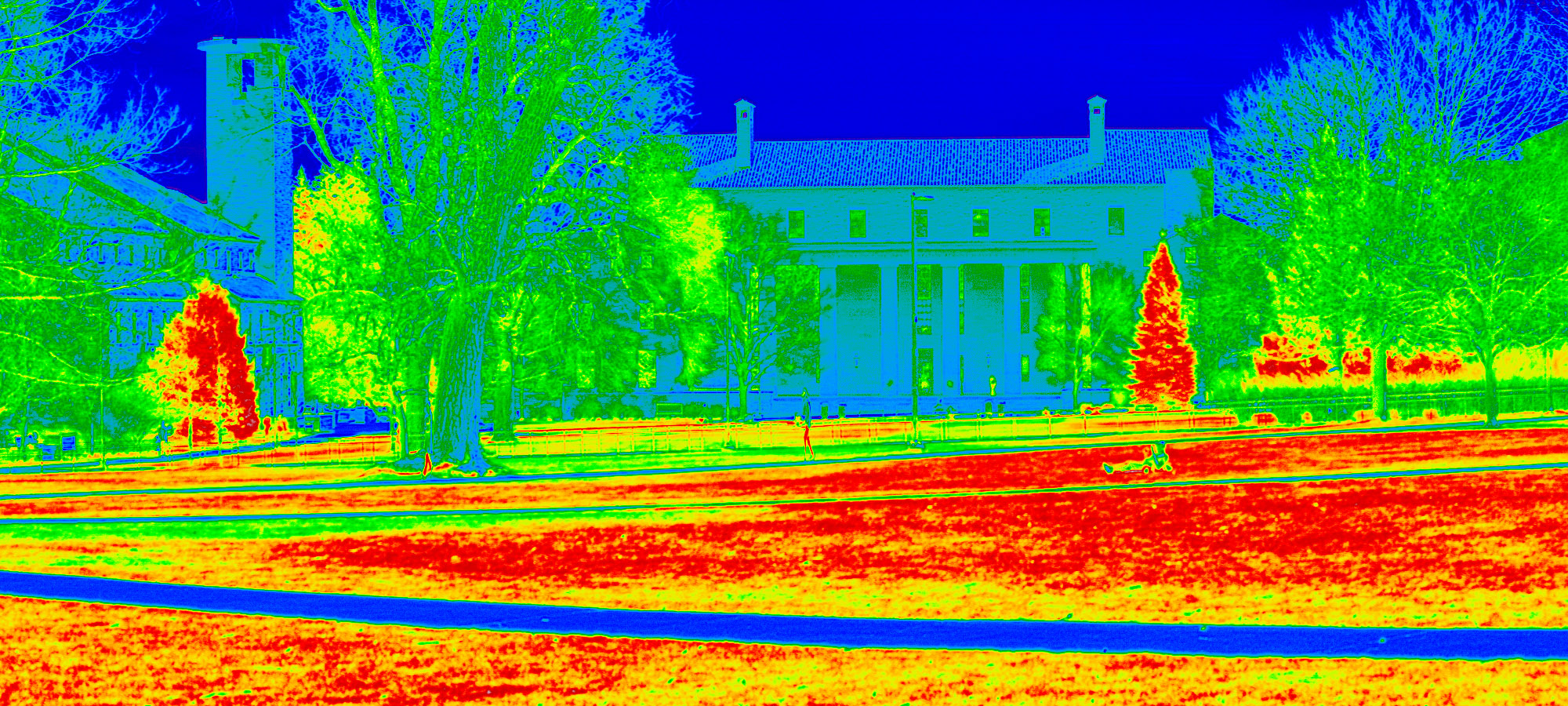
Multispectral analysis (MSI)
The basic principle of the optic spectrometry is the measurement of the properties of absorbance. reflectance or transparency that each material presents in distinct bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. An advantage of utilizing the Multispectral Imaging (MSI) technique is that the cameras can capture several square kilometers, depending on the size of the sensor, the distance from the camera to the objective, the utilized lens and the source of light. This flexibility of the MSI camera allows capturing large georeferenced landscapes or oblique. MSI cameras complement the potential of other sensors (such as LIDAR), and this is the main reason it is recommended that MSI photography is used at the beginning of each research to get an overview of the main features of the landscape.
The MSI technique is used regularly to propose identifications of geological deposits and vegetation through broad bands of wavelength, discrete and not contiguos: 1) Ultraviolet reflectance UVR (365-400 nm); 2) Visible spectrum VIS (400-780 nm); 3) Infrared IR (780-1100 nm); 4) Infrared reflectography IRR (1000-1700 nm); 5) False red infrared IRFC (476-1100 nm); 6) Normalized Difference Vegetation Index NDVI.